Introduction to the Cisco 200-301 Exam
In the ever-evolving world of networking, Cisco certifications hold immense value for IT professionals looking to advance their careers. Among the most sought-after certifications is the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) certification, which is validated by the 200-301 exam. This exam is a fundamental stepping stone for individuals aiming to establish themselves in networking roles, as it covers a wide range of networking concepts, protocols, and technologies.
The Cisco 200-301 exam tests candidates on various topics, including network fundamentals, security, automation, and IP services. Understanding core concepts such as IPv4 and IPv6 addressing, subnetting, routing protocols, and network automation is crucial for passing this Exam Dumps. One such important topic is the Extended Unique Identifier (EUI)-64 process, which plays a vital role in IPv6 addressing.
Definition of Cisco 200-301 Exam
The Cisco 200-301 Exam is a certification exam that serves as a prerequisite for obtaining the CCNA certification. This exam is designed to test an individual's knowledge of networking fundamentals, IP connectivity, security fundamentals, automation, and programmability. Candidates are required to demonstrate proficiency in configuring, managing, and troubleshooting network devices, making it an essential certification for aspiring network engineers.
The exam is structured with multiple-choice questions, simulations, and drag-and-drop questions, ensuring that candidates possess both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. A strong grasp of IPv6 concepts, including EUI-64, is necessary for anyone preparing for the 200-301 exam.
Components Used in the EUI-64 Process
EUI-64 (Extended Unique Identifier 64) is a method used to generate a unique 64-bit IPv6 interface identifier from a 48-bit MAC address. This technique plays a crucial role in IPv6 address auto-configuration, allowing network devices to derive their own unique addresses without requiring manual intervention.
To understand the EUI-64 process, it is essential to know its key components:
- MAC Address (Media Access Control Address): A 48-bit hardware address assigned to a network interface card (NIC) by the manufacturer. It consists of an Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) and a unique identifier assigned by the manufacturer.
- IPv6 Prefix: A 64-bit network identifier that defines the subnet to which a device belongs.
- FFFE Insertion: A fixed 16-bit value inserted in the middle of the MAC address to expand it from 48 bits to 64 bits.
- Inversion of the Universal/Local (U/L) Bit: The 7th bit of the first byte of the MAC address is flipped to indicate whether the address is universally or locally administered.
These components work together to ensure that every device has a unique and globally routable IPv6 address when using EUI-64.
Steps to Generate an IPv6 Interface ID Using EUI-64
The EUI-64 process involves several steps to convert a MAC address into a valid IPv6 interface identifier. Below is a step-by-step breakdown of how this transformation occurs:
- Obtain the MAC Address: The device's unique 48-bit MAC address is retrieved.
- Divide the MAC Address into Two Halves: The MAC address is split into two 24-bit halves.
- Insert the FFFE Value: The hexadecimal value FFFE is inserted between the two halves, expanding the address to 64 bits.
- Flip the U/L Bit: The 7th bit of the first byte is flipped (changed from 0 to 1 or vice versa) to indicate the uniqueness of the address.
- Form the Full IPv6 Address: The newly formed interface ID is combined with the network prefix to create a complete IPv6 address.
For example, if a device has a MAC address of 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E, the EUI-64 process would generate the following interface identifier:
- MAC Address: 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E
- Split into Two Halves: 00:1A:2B and 3C:4D:5E
- Insert FFFE: 00:1A:2B:FF:FE:3C:4D:5E
- Flip the U/L Bit: 02:1A:2B:FF:FE:3C:4D:5E
- Full IPv6 Address (Example with Prefix 2001:DB8::/64): 2001:DB8::021A:2BFF:FE3C:4D5E
Advantages and Disadvantages of EUI-64
Advantages:
- Automation: Devices can generate unique IPv6 addresses automatically without the need for manual configuration.
- Global Uniqueness: Ensures that each address is unique across networks due to its derivation from the MAC address.
- Scalability: Suitable for large networks where manually assigning IP addresses would be inefficient.
- Ease of Configuration: Reduces administrative overhead by eliminating the need for manually assigned static addresses.
Disadvantages:
- Privacy Concerns: Since EUI-64-based addresses are derived from MAC addresses, they can reveal device information and facilitate tracking.
- Predictability: Attackers can determine a device’s MAC address and target it based on its IPv6 address.
- Compatibility Issues: Some networks may prefer random IPv6 interface identifiers instead of those generated using EUI-64.
Alternatives to EUI-64 in IPv6 Addressing
Due to privacy concerns and predictability, several alternatives to EUI-64 exist in IPv6 addressing. These include:
- Randomly Generated IPv6 Addresses: Some operating systems generate random interface identifiers instead of using EUI-64 to enhance privacy.
- Temporary IPv6 Addresses: Devices can use temporary addresses for outgoing connections, reducing traceability.
- Manually Assigned IPv6 Addresses: Administrators can manually assign addresses to improve security and control.
- DHCPv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6): Allows centralized control over IPv6 address assignments rather than relying on automatic generation.
Conclusion
The Cisco 200-301 exam is a critical certification for networking professionals, covering essential topics such as IPv6 addressing and EUI-64. Understanding the EUI-64 process is crucial for network automation and ensuring unique addressing. While EUI-64 provides benefits such as automation and scalability, it also raises privacy concerns that have led to alternative approaches in IPv6 addressing.
Aspiring CCNA candidates should have a deep understanding of EUI-64, its benefits, drawbacks, and alternatives to make informed decisions in real-world networking scenarios. Mastering these concepts will not only help in passing the Cisco 200-301 exam but also in efficiently managing modern network infrastructures.
For high-quality Cisco 200-301 practice tests, study materials, and dumps, visit DumpsBoss your trusted resource for exam preparation!
Special Discount: Offer Valid For Limited Time “Cisco 200-301 Dumps” Order Now!
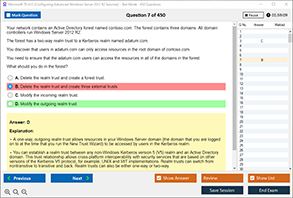
Sample Questions for Cisco 200-301 Dumps
Actual exam question from Cisco 200-301 Exam.
What is used in the EUI-64 process to create an IPv6 interface ID on an IPv6-enabled interface?
A) A randomly generated 64-bit number
B) The MAC address of the interface
C) A DHCPv6-assigned identifier
D) The IPv4 address of the interface