Overview of the CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 Exam
The CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 exam is a globally recognized certification for entry-level cybersecurity professionals. It validates the foundational knowledge and skills required to perform core security functions and pursue a career in IT security. The SY0-701 exam covers a wide array of security-related topics including threat detection, risk mitigation, identity and access management, architecture and design, and cryptographic technologies. Understanding encryption, especially asymmetric encryption, is crucial for anyone aiming to pass this exam successfully.
DumpsBoss provides a comprehensive selection of resources tailored for the CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 exam. These include expertly crafted practice tests, updated dumps, and study guides to help candidates understand key concepts such as encryption technologies thoroughly. Using DumpsBoss can give you a distinct advantage in your preparation and boost your confidence before taking the exam.
Basics of Encryption Technologies
Encryption is the process of converting plaintext data into ciphertext to protect it from unauthorized access. This process ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to anyone who doesn't possess the decryption key. There are two main types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric.
Encryption technologies are critical in safeguarding sensitive information, maintaining data integrity, and ensuring secure communication across networks. Whether it’s for personal communications, enterprise-level data storage, or transmitting information over the internet, encryption is a cornerstone of cybersecurity.
The CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 exam places significant emphasis on understanding different encryption methods, their applications, and how to deploy them effectively within an organization. Mastering encryption fundamentals is therefore essential for any aspiring security professional.
What is Asymmetric Encryption Technology?
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, uses a pair of keys for encryption and decryption: a public key and a private key. The public key is openly distributed and can be used by anyone to encrypt a message, but only the corresponding private key can decrypt it.
This method solves many of the challenges associated with symmetric encryption, particularly key distribution. Because the public key can be shared freely without compromising security, asymmetric encryption is ideal for situations where secure key exchange is difficult or impractical.
The mathematical algorithms used in asymmetric encryption are complex and designed to make it computationally infeasible to derive the private key from the public key. This makes asymmetric encryption highly secure for various applications, including digital signatures, secure email, and HTTPS communication.
Key Features of Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption offers several distinct features that make it indispensable in modern cybersecurity:
-
Two-Key System: Uses a public and a private key, eliminating the need for secure key exchange channels.
-
Enhanced Security: Since the private key is never shared, it provides robust protection against interception.
-
Digital Signatures: Enables authentication and data integrity by allowing messages to be signed with a private key and verified with a public key.
-
Scalability: Easier to manage in large environments where multiple parties need to communicate securely.
-
Non-repudiation: Ensures that the sender of a message cannot deny sending it, thanks to the unique digital signature created by the private key.
These features are not only theoretical but are practically applied in real-world cybersecurity protocols and systems. Understanding them is vital for passing the Security+ SY0-701 exam.
Examples and Use Cases
Asymmetric encryption is widely used in numerous applications and services that require secure communication and data protection. Some common examples include:
-
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)/Transport Layer Security (TLS): Used in HTTPS protocols to secure communications over the web. The server presents a public key to initiate a secure session.
-
Email Encryption (PGP/GPG): Ensures secure email communication by encrypting messages with the recipient’s public key and decrypting them with their private key.
-
Digital Signatures: Used in software distribution to ensure that the code has not been tampered with. Developers sign the software with their private key, and users verify it with the public key.
-
Cryptocurrency Wallets: Wallets use asymmetric encryption to secure transactions. The public key is the address used to receive funds, and the private key authorizes outgoing transactions.
-
VPNs and Secure Tunnels: Asymmetric encryption is used during the key exchange phase to establish a secure session.
These use cases underscore the importance of understanding asymmetric encryption, especially for those preparing for the SY0-701 exam. DumpsBoss provides real-world examples and practice questions to solidify your understanding of such applications.
Comparison Table: Asymmetric vs. Symmetric Encryption
| Feature | Asymmetric Encryption | Symmetric Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Key Type | Public and private key pair | Single shared secret key |
| Speed | Slower due to complex algorithms | Faster due to simpler computations |
| Key Distribution | Easy (public key can be shared openly) | Difficult (requires secure exchange) |
| Use Cases | Digital signatures, HTTPS, email, etc. | File encryption, VPN data streams |
| Security Level | High (difficult to derive private key) | Moderate (key compromise = breach) |
| Resource Intensity | More resource-intensive | Less resource-intensive |
| Scalability | High | Low (managing many keys is complex) |
| Example Algorithms | RSA, ECC, DSA | AES, DES, 3DES |
This comparison clearly highlights the strengths and limitations of both encryption types. For the SY0-701 exam, you will be expected to recognize when to apply each type effectively. DumpsBoss provides detailed explanations and practice scenarios that help candidates become proficient in such distinctions.
Conclusion
Encryption is a fundamental pillar of cybersecurity, and understanding its various forms is essential for any IT security professional. Asymmetric encryption, in particular, plays a crucial role in securing communications, authenticating users, and maintaining data integrity in today’s digital landscape.
For candidates preparing for the CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 exam, mastering asymmetric encryption is non-negotiable. It not only strengthens your theoretical knowledge but also enhances your practical skills in real-world scenarios. The two-key system, secure key distribution, digital signatures, and public-key infrastructure (PKI) are all topics that will appear on the exam.
DumpsBoss is an invaluable resource for mastering these complex concepts. With expertly curated study guides, up-to-date exam dumps, and real-world practice questions, DumpsBoss equips you with everything needed to pass the SY0-701 exam with confidence. Whether you're just beginning your cybersecurity journey or looking to validate your knowledge, DumpsBoss ensures you're fully prepared to meet and exceed the exam requirements.
Start your journey today with DumpsBoss and take the next step toward becoming a certified cybersecurity professional. A strong grasp of encryption technologies, especially asymmetric encryption, will help you ace the exam and lay a solid foundation for a successful career in information security.
Special Discount: Offer Valid For Limited Time “CompTIA SY0-701 Dumps” Order Now!
Sample Questions for CompTIA 220-1101 Exam Dumps
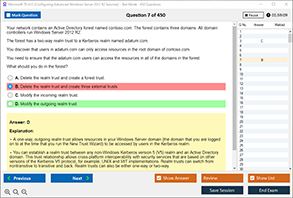
Actual exam question from CompTIA 220-1101 Exam.
What is an accurate description of asymmetric encryption technology?
A) It uses a single key for both encryption and decryption
B) It relies on secret algorithms known only to the sender and receiver
C) It uses a pair of keys: one public and one private
D) It encrypts data using only a shared password