Introduction to Cisco 200-301 Exam
In today's digital era, networking plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless communication across various platforms. The Cisco 200-301 certification, also known as the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) exam, is an industry-recognized credential that validates an individual's networking skills and knowledge. As businesses continue to expand their networks, professionals with a strong understanding of Wi-Fi standards and networking fundamentals are in high demand. This blog will delve into the definition of the Cisco 200-301 exam, explore different Wi-Fi standards operating in the 2.4 GHz band, compare these standards, and discuss their significance.
Definition of Cisco 200-301 Exam
The Cisco 200-301 exam is a globally recognized certification designed for individuals looking to establish or advance their careers in networking. This exam tests a candidate's ability to configure, manage, and troubleshoot networks, along with a solid understanding of security, automation, and wireless networking concepts. One of the essential topics covered in the Exam Dumps is Wi-Fi standards, specifically those operating in the 2.4 GHz band. Understanding these standards is critical for network engineers and IT professionals to optimize wireless communication and ensure efficient connectivity.
Wi-Fi Standards Operating in the 2.4 GHz Band
The 2.4 GHz frequency band has been widely used in wireless networking due to its extensive coverage and ability to penetrate obstacles. Several Wi-Fi standards operate within this range, each offering varying data rates and improvements over previous versions. The primary standards in this category include IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g, and IEEE 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4).
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11b was one of the first widely adopted Wi-Fi standards operating in the 2.4 GHz band. Introduced in 1999, it offers a maximum data rate of 11 Mbps and uses direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) technology to minimize interference. While it provided significant improvements over earlier wireless technologies, its lower data rates and susceptibility to interference made it less favorable as newer standards emerged.
IEEE 802.11g
Launched in 2003, IEEE 802.11g improved upon its predecessor by offering speeds of up to 54 Mbps while maintaining backward compatibility with 802.11b. It employed orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM), which enhanced performance and efficiency. However, despite its higher speed, it still suffered from interference issues due to operating in the crowded 2.4 GHz frequency.
IEEE 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4)
IEEE 802.11n, commonly referred to as Wi-Fi 4, was introduced in 2009 and marked a significant leap in wireless networking. It supports data rates of up to 600 Mbps by utilizing multiple input multiple output (MIMO) technology. This standard improved range, speed, and efficiency while remaining compatible with both 802.11b and 802.11g. Due to its enhancements, Wi-Fi 4 remains a popular choice for many wireless networking applications.
Comparison of the Three Standards
Each of these Wi-Fi standards brought improvements over their predecessors. Below is a comparison of their key characteristics:
|
Standard |
Maximum Speed |
Year Introduced |
Modulation Technique |
Compatibility |
|
IEEE 802.11b |
11 Mbps |
1999 |
DSSS |
Legacy |
|
IEEE 802.11g |
54 Mbps |
2003 |
OFDM |
Backward compatible with 802.11b |
|
IEEE 802.11n |
600 Mbps |
2009 |
MIMO, OFDM |
Backward compatible with 802.11b/g |
Why These Standards Operate in the 2.4 GHz Range
The 2.4 GHz band has been a preferred choice for wireless networking due to its ability to provide broader coverage and penetrate obstacles such as walls and furniture. Some of the key reasons for using this frequency include:
- Longer Range: Compared to higher frequency bands, 2.4 GHz signals travel farther, making them suitable for large areas.
- Better Obstacle Penetration: Unlike 5 GHz signals, 2.4 GHz waves can pass through walls and other obstructions more effectively.
- Cost Efficiency: Devices operating in the 2.4 GHz band are generally more affordable and widely available.
- Legacy Support: Many older devices were designed to operate in this frequency range, ensuring backward compatibility with newer standards.
However, the widespread use of this band has also led to congestion and interference from other wireless technologies such as Bluetooth, microwaves, and cordless phones, prompting the need for alternative frequency bands.
Other Wi-Fi Standards and Their Frequency Ranges
While the 2.4 GHz band remains popular, newer Wi-Fi standards have introduced support for higher frequency bands to address congestion and enhance performance. Some notable standards include:
- IEEE 802.11a (Introduced in 1999, operates in the 5 GHz band, offers speeds up to 54 Mbps)
- IEEE 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) (Introduced in 2013, operates in the 5 GHz band, supports speeds up to 3.46 Gbps)
- IEEE 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) (Introduced in 2019, operates in both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, delivers up to 9.6 Gbps)
- IEEE 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) (Expected in the near future, operates in multiple frequency bands with speeds exceeding 40 Gbps)
These advancements highlight the industry's efforts to improve wireless connectivity, reduce interference, and enhance network performance.
Conclusion
Understanding Wi-Fi standards is essential for networking professionals, especially those pursuing Cisco 200-301 certification. The 2.4 GHz band has played a vital role in the evolution of wireless networking, with IEEE 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n serving as foundational standards. While these standards provided widespread connectivity, advancements in technology have led to the adoption of higher frequency bands to mitigate congestion and enhance performance. For aspiring network engineers, mastering these concepts is crucial for designing and optimizing modern wireless networks. By leveraging resources like DumpsBoss, candidates can gain the knowledge and practice they need to succeed in the Cisco 200-301 exam and advance their careers in the networking industry.
Special Discount: Offer Valid For Limited Time “200-301 Exam” Order Now!
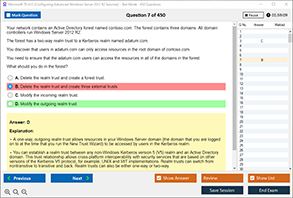
Sample Questions for Cisco 200-301 Dumps
Actual exam question from Cisco 200-301 Exam.
Which three Wi-Fi standards operate in the 2.4 GHz range of frequencies?
A) 802.11a, 802.11ac, 802.11ax
B) 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11n
C) 802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11ax
D) 802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11ad