Overview of the CompTIA 220-1101 Exam
The CompTIA 220-1101 exam, part of the CompTIA A+ certification, is a foundational certification for aspiring IT professionals. This exam tests a candidate's knowledge and skills in areas such as mobile devices, networking technology, hardware, virtualization, cloud computing, and network troubleshooting. As the first of two exams required for A+ certification, the 220-1101 validates the essential competencies needed for an entry-level IT support role.
For individuals preparing for this exam, understanding various types of network cabling, including coaxial cables, is crucial. The use of different media types, their characteristics, and specific applications are commonly featured on the exam. This is where DumpsBoss becomes an indispensable study partner. With up-to-date exam dumps, practice tests, and comprehensive study guides tailored to CompTIA standards, DumpsBoss helps candidates gain a deep understanding of technical topics, such as coaxial cabling, and improves their chances of success.
What is Coaxial Cable?
Coaxial cable, often referred to as "coax," is a type of electrical cable that transmits radio frequency (RF) signals. It is composed of four main layers:
-
Core Conductor: Typically made of copper or aluminum, the core is responsible for carrying the electrical signal.
-
Insulating Layer: This dielectric insulator surrounds the core and separates it from the shielding.
-
Shielding: A metallic shield (braid or foil) encases the insulator to protect the signal from electromagnetic interference (EMI).
-
Outer Jacket: The final layer is a plastic casing that protects the cable from physical damage and environmental conditions.
The design of coaxial cable allows it to transmit data over long distances with minimal signal loss and high resistance to interference. This makes it ideal for applications where signal integrity is critical.
Two Suitable Applications for Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables are still widely used in certain modern applications due to their unique properties. Two suitable and common applications include:
-
Cable Television (CATV): Coaxial cables are extensively used in the delivery of cable television services. The high bandwidth and resistance to EMI make them ideal for transmitting multiple channels with minimal degradation. Coaxial cable runs from the service provider's main line to the customer's set-top box, ensuring consistent signal quality.
-
Internet via Cable Modems: In many residential settings, Internet services are delivered through coaxial cable using DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification) standards. Coaxial cable connects the cable modem to the service provider’s network, enabling high-speed broadband connections that support streaming, gaming, and large downloads.
These use cases highlight the ongoing relevance of coaxial cables in modern telecommunications, particularly in home entertainment and Internet connectivity.
Other Less Common or Legacy Uses
Although coaxial cable is not as dominant in enterprise network infrastructures today, it has a long history of use in various legacy systems. Some of these include:
-
10BASE2 and 10BASE5 Ethernet Networks: These are older Ethernet standards that relied on coaxial cables (RG-58 and RG-8, respectively) for data transmission in local area networks (LANs). These networks have largely been replaced by twisted-pair Ethernet (e.g., Cat5e, Cat6) due to better scalability and ease of maintenance.
-
Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV): Analog CCTV systems often used coaxial cable to transmit video signals from cameras to monitors and recording devices. While IP-based surveillance systems are more prevalent today, many existing analog installations still rely on coaxial cabling.
-
Radio and Ham Radio Communications: Coaxial cable has long been used in amateur (ham) radio setups to connect antennas to transceivers. Its shielding and durability make it suitable for transmitting RF signals over moderate distances.
-
Medical Equipment: Some medical imaging and monitoring equipment still use coaxial cable for transmitting data due to its ability to shield signals from external noise, which is crucial in medical environments.
These legacy applications demonstrate the versatility of coaxial cables and their historical importance in network and communication technologies.
Coaxial Cable vs. Other Cabling Options
To fully understand where coaxial cable stands today, it’s essential to compare it with other modern cabling solutions:
-
Twisted Pair Cable (Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7):
-
Advantages: Lower cost, easier to install, supports high data rates (up to 10 Gbps for Cat6a), and is widely used in LANs.
-
Disadvantages: Shorter maximum distance than coax (typically up to 100 meters).
-
Common Uses: Ethernet networking, VoIP systems.
-
-
Fiber Optic Cable:
-
Advantages: Extremely high bandwidth, immune to EMI, supports long-distance transmission.
-
Disadvantages: Higher cost, more fragile, requires specialized installation.
-
Common Uses: Backbone network connections, data centers, long-distance telecommunications.
-
-
Coaxial Cable:
-
Advantages: Strong resistance to interference, good for long-distance transmission without amplifiers, robust and durable.
-
Disadvantages: Bulkier than twisted pair, more expensive, not suitable for high-speed digital networking compared to fiber.
-
Common Uses: Cable TV, Internet via cable modem, CCTV.
-
While coaxial cable offers excellent performance in certain use cases, it has been overshadowed in enterprise networking by twisted pair and fiber optic cables due to their scalability and performance advantages.
Why This Question Matters for the CompTIA 220-1101 Exam
Understanding coaxial cable and its applications is not just about historical knowledge—it has practical implications in the CompTIA 220-1101 exam. Questions related to media types and their characteristics are a recurring theme on the exam, especially in the networking and hardware domains.
-
Identification and Differentiation: Candidates are expected to recognize different cable types based on their physical characteristics and performance metrics. This includes understanding connectors like BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman) and F-type used with coaxial cables.
-
Appropriate Usage: Test-takers must know when and where to use coaxial cables versus other types. This includes identifying scenarios where coax is still relevant, such as cable Internet and CATV systems.
-
Troubleshooting and Installation: The exam includes troubleshooting cable issues. Recognizing signal degradation, interference, and connector issues specific to coaxial cable can be a valuable skill.
-
Legacy System Knowledge: While modern systems may not rely on coaxial cable, many environments still support legacy systems. Being familiar with coaxial cable allows IT professionals to maintain or upgrade these older systems efficiently.
DumpsBoss ensures that candidates are well-prepared to tackle such questions. The platform offers realistic practice exams and verified questions that reflect the current 220-1101 exam format. This targeted preparation strategy helps learners become confident in answering questions about coaxial cables and their role in modern and legacy networks.
Conclusion
Coaxial cable, though considered a legacy medium in many contexts, remains relevant in several modern applications, including cable TV and broadband Internet delivery. Its unique construction allows it to transmit data with minimal signal loss and excellent interference protection, making it ideal for specific use cases.
For CompTIA 220-1101 candidates, understanding coaxial cable is not only important for passing the exam but also for working in real-world IT environments. The ability to differentiate between various cabling options, identify appropriate use cases, and troubleshoot issues is crucial for a well-rounded IT professional.
DumpsBoss plays a vital role in supporting candidates on this journey. With expertly crafted resources, up-to-date exam dumps, and in-depth guides, DumpsBoss ensures that learners have access to everything they need to succeed. Whether you're revisiting foundational topics or preparing for exam day, DumpsBoss is your trusted partner for mastering the CompTIA 220-1101 exam.
By focusing on practical applications and aligning study materials with exam objectives, DumpsBoss empowers aspiring IT professionals to achieve certification success and build a strong foundation for their careers in information technology.
Special Discount: Offer Valid For Limited Time “CompTIA 220-1101 Dumps” Order Now!
Sample Questions for CompTIA 220-1101 Exam Dumps
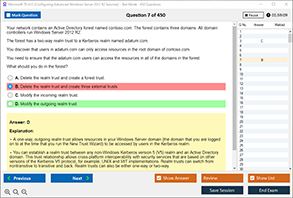
Actual exam question from CompTIA 220-1101 Exam.
Which two applications are suitable for deploying coaxial cables? (Choose two.)
A) Cable television (CATV)
B) Fiber-optic backbone connections
C) Traditional Ethernet (10BASE2/10BASE5)
D) Wireless access points
E) VoIP phone systems