Overview of CompTIA SY0-701 Exam
The CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 certification exam is a globally recognized credential that validates the foundational skills and knowledge necessary for a successful career in cybersecurity. As a pivotal certification in the CompTIA cybersecurity pathway, the SY0-701 covers essential security topics including threats, attacks, vulnerabilities, architecture and design, implementation, operations and incident response, and governance, risk, and compliance.
One of the critical areas tested in the SY0-701 exam is access control—the process of regulating who or what can view or use resources in a computing environment. Mastering the principles of access control is essential for any IT security professional aiming to prevent unauthorized access, protect sensitive data, and maintain overall system integrity. DumpsBoss serves as an invaluable resource for exam preparation, offering expertly curated study materials, real exam dumps, and practice tests to ensure candidates are well-prepared and confident on exam day.
Definition of Access Control
Access control is a security technique that regulates who or what can access or use resources in a computing environment. It is a fundamental concept in cybersecurity and is used to protect systems from unauthorized access and ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Access control involves three primary elements:
-
Authentication – Verifying the identity of a user or system.
-
Authorization – Granting or denying permissions to resources based on authenticated identities.
-
Accounting – Tracking what authenticated and authorized users do while accessing systems.
These three principles form the core of access control and are often abbreviated as AAA. They work together to secure data, manage user privileges, and audit system usage. Understanding these concepts is vital for anyone taking the CompTIA SY0-701 exam, as questions on access control frequently appear in various forms.
The First Line of Defense: Authentication Mechanisms
Authentication is the first and arguably the most crucial line of defense in access control. It is the process of validating the identity of a user, device, or entity before granting access to resources. Effective authentication mechanisms ensure that only legitimate users can access sensitive systems.
There are several types of authentication mechanisms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
-
Password-Based Authentication: The most common method, involving a user ID and password combination. While easy to implement, it is susceptible to brute-force attacks, phishing, and poor password practices.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Combines two or more authentication factors such as:
-
Something you know (password)
-
Something you have (smartphone, token)
-
Something you are (biometrics) MFA significantly enhances security and is highly recommended.
-
-
Biometric Authentication: Uses unique physical characteristics like fingerprints, facial recognition, or retina scans. It provides high security but can raise privacy concerns and is dependent on specialized hardware.
-
Token-Based Authentication: Uses physical or digital tokens (e.g., RSA SecurID) that generate time-sensitive codes for login. These are commonly used in enterprise environments.
-
Certificate-Based Authentication: Involves the use of digital certificates to establish credentials. It is commonly used in VPNs and secure email communications.
-
Single Sign-On (SSO): Allows users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple systems. It improves user experience and reduces password fatigue but introduces a single point of failure.
Understanding and implementing robust authentication mechanisms is critical for any cybersecurity professional. For candidates preparing for the SY0-701 exam, DumpsBoss provides detailed breakdowns and practice questions to help master this domain.
Additional Protective Measures (Secondary Defenses)
While authentication is the frontline defense, additional layers of protection are essential to create a comprehensive security posture. These secondary defenses include:
-
Authorization Controls: Once a user is authenticated, authorization determines what resources they can access and what actions they can perform. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), and Discretionary Access Control (DAC) are common models.
-
Access Control Lists (ACLs): These define permissions attached to objects, specifying which users or system processes can access the objects and what operations they can perform.
-
Encryption: Encrypting data ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains unreadable without the proper decryption key. Both data-at-rest and data-in-transit should be encrypted.
-
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): These systems monitor network and system activities for malicious activity and policy violations, adding another layer of defense.
-
Audit Logs and Monitoring: Keeping detailed logs of access and activities can help identify suspicious behavior, ensure compliance, and facilitate forensic investigations.
-
Network Segmentation: Dividing a network into segments limits access to sensitive information and helps contain breaches.
-
Physical Security Controls: Often overlooked, physical barriers and surveillance prevent unauthorized physical access to critical systems and infrastructure.
For aspiring cybersecurity professionals, understanding these layered defenses is not just important for passing the SY0-701 exam but also for implementing real-world security solutions. DumpsBoss excels in providing scenario-based practice questions that incorporate these secondary defense mechanisms.
Why the First Line of Defense Matters
The first line of defense, authentication, is the gateway to all systems and data. If this line is breached, the entire security infrastructure becomes vulnerable. Strong authentication prevents unauthorized access, reduces the risk of data breaches, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI-DSS.
Key reasons why the first line of defense matters include:
-
Prevention of Identity Theft: Verifying identity ensures attackers cannot impersonate legitimate users.
-
Protection of Sensitive Data: Prevents unauthorized users from accessing confidential information.
-
Minimized Attack Surface: Reduces the number of potential entry points for attackers.
-
Enhanced User Accountability: Ensures actions can be traced back to authenticated users.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Meets requirements set by data protection laws and industry regulations.
Given the critical importance of authentication, it is heavily emphasized in the SY0-701 exam. DumpsBoss provides in-depth tutorials and question banks that focus on real-world applications and best practices in authentication.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Despite its importance, access control is often misconfigured or misunderstood. Common mistakes and misconceptions include:
-
Weak Password Policies: Allowing short or simple passwords increases vulnerability to attacks.
-
Overprivileged Accounts: Granting users more access than needed violates the principle of least privilege.
-
Ignoring Physical Security: Failing to secure physical access points can compromise even the best digital controls.
-
Single Factor Authentication: Relying solely on passwords without additional factors is insufficient.
-
Inadequate Monitoring: Not logging or reviewing access activities makes it harder to detect breaches.
-
Misuse of SSO: Poorly implemented Single Sign-On solutions can become a single point of failure.
-
Failure to Revoke Access: Not deactivating accounts when employees leave can create backdoors for attackers.
Avoiding these mistakes is crucial for maintaining a strong security posture. DumpsBoss equips exam candidates with real-life examples and solutions to these common pitfalls, ensuring not just exam success but also workplace competency.
Conclusion
Access control is a foundational element of cybersecurity and a core topic in the CompTIA SY0-701 exam. From understanding the basics of authentication to implementing multi-layered defense mechanisms, mastering access control is vital for aspiring security professionals.
The first line of defense—authentication—plays a critical role in securing systems and data. However, a holistic approach that includes secondary defenses, regular monitoring, and adherence to best practices is essential for comprehensive protection.
For candidates preparing for the SY0-701 exam, DumpsBoss offers a superior suite of learning resources, including up-to-date exam dumps, detailed tutorials, and realistic practice tests. By leveraging DumpsBoss, learners can confidently navigate the complexities of access control and ace their certification exam, setting the stage for a successful cybersecurity career.
With DumpsBoss, your journey to becoming a certified cybersecurity professional is not only achievable but also deeply informed and well-supported.
Special Discount: Offer Valid For Limited Time “SY0-701 Dumps” Order Now!
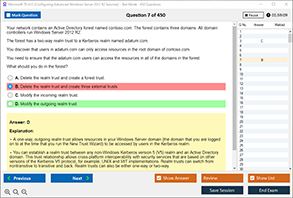
Sample Questions for CompTIA SY0-701 Exam Dumps
Actual exam question from CompTIA SY0-701 Exam.
What is the first line of defense to protect a device from improper access control?
A) Antivirus software
B) User authentication
C) Firewall
D) Encryption