Overview of CompTIA SY0-701 (Security+) Exam
The CompTIA SY0-701, commonly known as the Security+ exam, is a globally recognized cybersecurity certification designed to validate a candidate's foundational knowledge and skills in security. As cyber threats continue to evolve, this certification ensures that professionals can identify, mitigate, and respond to various security issues, including those posed by malicious code.
Targeting IT professionals, security administrators, and network technicians, the SY0-701 covers critical topics like threat detection, risk management, incident response, architecture and design, and governance. One of the key areas emphasized is the identification and prevention of malicious code—a crucial skill in modern cybersecurity. DumpsBoss offers updated study materials, exam dumps, and practice tests that reflect the latest exam objectives and are tailored to help candidates grasp such complex topics effectively.
Defining Malicious Code
Malicious code, often referred to as malware, is any software or script designed to cause harm, steal data, or exploit a system's resources without the user's knowledge or consent. Unlike benign software, malicious code operates covertly and often embeds itself into legitimate programs or files to avoid detection.
This broad term encompasses various forms of harmful software, from traditional computer viruses and worms to advanced threats like ransomware and spyware. Malicious code is a primary vector for cyberattacks, targeting both individual users and organizations to compromise data integrity, availability, and confidentiality.
Common Types of Malicious Code Found on User Devices
Understanding the types of malicious code is vital for any cybersecurity professional. Below are the most common forms found on user devices:
-
Viruses:
-
Attach themselves to legitimate files or programs.
-
Spread when the infected program is executed.
-
Can corrupt, delete, or steal data.
-
-
Worms:
-
Self-replicating malware that spreads across networks.
-
Does not need a host file.
-
Can cause network congestion and system failures.
-
-
Trojans:
-
Disguised as legitimate software.
-
Often create backdoors for unauthorized access.
-
Common in phishing attacks.
-
-
Ransomware:
-
Encrypts a user's data and demands a ransom.
-
Commonly delivered through email attachments or malicious websites.
-
Highly disruptive and costly.
-
-
Spyware:
-
Secretly monitors user activity.
-
Collects sensitive information such as login credentials and credit card numbers.
-
-
Adware:
-
Automatically displays unwanted ads.
-
May include tracking features to monitor user behavior.
-
-
Rootkits:
-
Gain unauthorized root or administrative access.
-
Often used to hide other malicious activities.
-
-
Keyloggers:
-
Record keystrokes to capture sensitive information.
-
Often used in identity theft attacks.
-
Recognizing these malware types is essential not just for the exam but also for real-world defense.
Symptoms of Malicious Code on Devices
Malicious code is designed to remain hidden, but it often leaves behind telltale signs. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for prompt detection and response:
-
Sluggish Performance:
-
A sudden drop in system speed.
-
Programs taking longer to load or crashing frequently.
-
-
Unusual Pop-ups:
-
Frequent, unsolicited advertisements or warnings.
-
Redirects to suspicious websites.
-
-
Unrecognized Programs:
-
Unknown applications appearing in task manager.
-
Programs launching on startup without user action.
-
-
System Crashes and Freezes:
-
Blue screen errors.
-
Inability to reboot or log in.
-
-
Disabled Security Software:
-
Antivirus or firewall suddenly turned off.
-
Inability to update or launch security applications.
-
-
Unusual Network Activity:
-
High data usage with no user-initiated activity.
-
Connections to unfamiliar IP addresses.
-
-
Data Loss or Corruption:
-
Files missing, encrypted, or corrupted.
-
System settings changed without user input.
-
-
Unauthorized Access Attempts:
-
Account lockouts.
-
Login attempts from unknown locations or devices.
-
Detecting these symptoms early can significantly reduce damage and recovery time.
How Malicious Code Affects User Devices and Organizations
The impact of malicious code extends beyond inconvenience. It can cause severe consequences for both individual users and organizations:
-
Data Breaches:
-
Loss of sensitive information like financial data, personal IDs, and proprietary information.
-
Leads to identity theft or intellectual property theft.
-
-
Financial Losses:
-
Ransom payments, regulatory fines, or loss of business.
-
Costs related to data recovery and system restoration.
-
-
Reputation Damage:
-
Customers lose trust in a business after a malware-related incident.
-
Negative media coverage and customer attrition.
-
-
Operational Disruptions:
-
Downtime in critical systems.
-
Interruptions in service delivery or manufacturing processes.
-
-
Legal Consequences:
-
Non-compliance with data protection laws like GDPR or HIPAA.
-
Potential lawsuits from affected customers or partners.
-
-
Loss of Productivity:
-
Time spent dealing with infected systems.
-
Employee downtime while systems are restored.
-
-
Resource Drain:
-
IT teams diverted to deal with malware instead of business goals.
-
Increased demand on security infrastructure and personnel.
-
Exam-Focused Perspective (SY0-701)
The SY0-701 exam places strong emphasis on understanding, identifying, and mitigating malicious code. Questions in the exam may ask candidates to:
-
Differentiate Between Types of Malware:
-
Know the behavior, targets, and impact of each malware type.
-
-
Analyze Security Logs:
-
Detect anomalies or indicators of compromise that point to malware infections.
-
-
Implement Security Controls:
-
Suggest or apply effective preventive measures like endpoint protection, patch management, and network segmentation.
-
-
Perform Risk Assessments:
-
Evaluate threats based on potential malware vectors and develop risk mitigation strategies.
-
-
Respond to Incidents:
-
Apply incident response procedures in case of malware outbreaks.
-
-
Understand Attack Vectors:
-
Phishing, drive-by downloads, USB attacks, and more.
-
-
Use Malware Analysis Tools:
-
Know basic functions of tools like sandbox environments, antivirus software, and behavioral analysis systems.
-
To master these exam objectives, using DumpsBoss can significantly boost your preparation. DumpsBoss provides updated exam questions, scenario-based practice, and topic-specific resources that align perfectly with SY0-701 objectives.
Best Practices for Preventing Malicious Code
Preventing malicious code is a multi-layered strategy involving users, software, and network defense measures. Here are some proven best practices:
-
Keep Software Updated:
-
Regularly patch operating systems and applications.
-
Fix known vulnerabilities before they're exploited.
-
-
Use Reliable Antivirus and Anti-Malware Tools:
-
Implement reputable endpoint protection solutions.
-
Schedule regular scans and enable real-time protection.
-
-
Enable Firewalls:
-
Use host-based and network-based firewalls.
-
Monitor inbound and outbound traffic.
-
-
Educate Users:
-
Conduct regular training on phishing and safe browsing.
-
Promote strong password practices.
-
-
Implement Email Security:
-
Use spam filters and attachment scanning.
-
Employ DKIM, DMARC, and SPF to verify senders.
-
-
Apply Network Segmentation:
-
Isolate critical systems from user networks.
-
Use VLANs and access control lists (ACLs).
-
-
Regular Backups:
-
Automate backups of critical data.
-
Store copies offline or in secure cloud locations.
-
-
Restrict Admin Privileges:
-
Use role-based access control.
-
Limit admin rights to only necessary personnel.
-
-
Monitor and Audit Logs:
-
Use SIEM tools to analyze logs.
-
Set up alerts for suspicious activities.
-
-
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
-
Add extra layers of security for accessing systems.
-
By adopting these practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of malware infections.
Conclusion
Malicious code remains one of the most persistent and dangerous threats in cybersecurity. Whether it's a simple keylogger or a sophisticated ransomware variant, the impact on user devices and organizational systems can be devastating. Recognizing, detecting, and preventing these threats is essential for maintaining data integrity and security.
The CompTIA SY0-701 exam ensures that professionals are equipped with the knowledge and skills to combat these threats effectively. Candidates preparing for the exam must understand various types of malicious code, recognize symptoms of infection, and implement effective defense mechanisms.
DumpsBoss serves as an invaluable resource for exam preparation. With up-to-date exam dumps, real-world practice questions, and comprehensive study guides, DumpsBoss empowers candidates to succeed in the SY0-701 exam and become confident cybersecurity professionals. Embracing such resources ensures a well-rounded understanding of malicious code and strengthens readiness to protect systems in real-world environments.
Special Discount: Offer Valid For Limited Time “SY0-701 Dumps” Order Now!
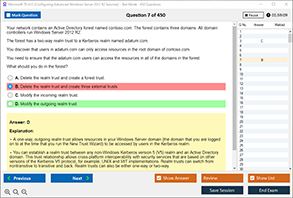
Sample Questions for CompTIA SY0-701 Exam Dumps
Actual exam question from CompTIA SY0-701 Exam.
Which option describes malicious code running on user devices?
A) Phishing
B) Firewall
C) Malware
D) Encryption